Egypt, a land of ancient mysteries and enduring fascination, has captivated the world for millennia. Nestled along the banks of the Nile River, this ancient civilization flourished for thousands of years, leaving behind a rich legacy of art, architecture, and culture.
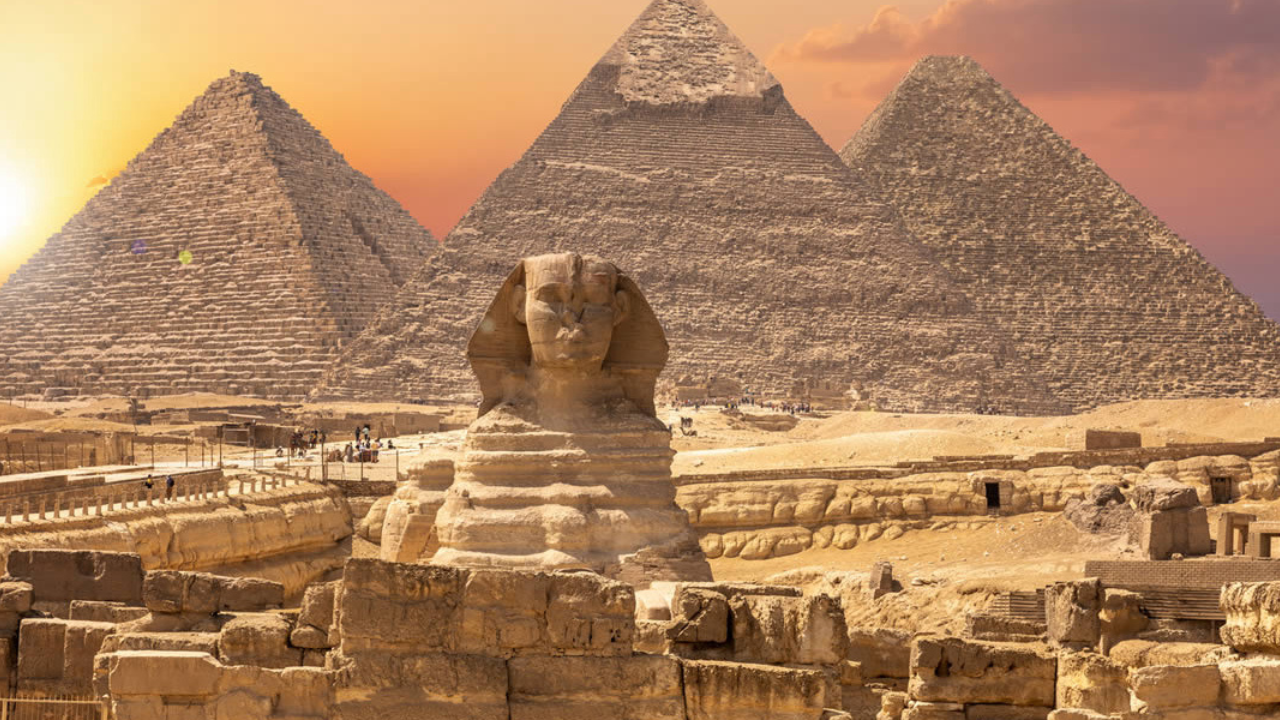

From the towering pyramids to the enigmatic hieroglyphs, Ancient Egypt continues to intrigue and inspire us today.
The Rise of the Pharaohs
The history of Ancient Egypt is marked by the rule of powerful pharaohs, who were considered divine rulers and intermediaries between the gods and the people.

These pharaohs oversaw the construction of magnificent temples, pyramids, and other monumental structures, as well as the development of a complex system of government and administration.
- Divine rule of the pharaohs: Pharaohs were believed to be divine beings and intermediaries between the gods and the people.
- Construction of monumental structures: The pharaohs oversaw the building of pyramids, temples, and other impressive structures.
- Development of a complex system of government: The Egyptian government was highly organized and efficient, with a hierarchy of officials and bureaucrats.
The Pyramids: Marvels of Engineering
One of the most iconic symbols of Ancient Egypt is the pyramids,
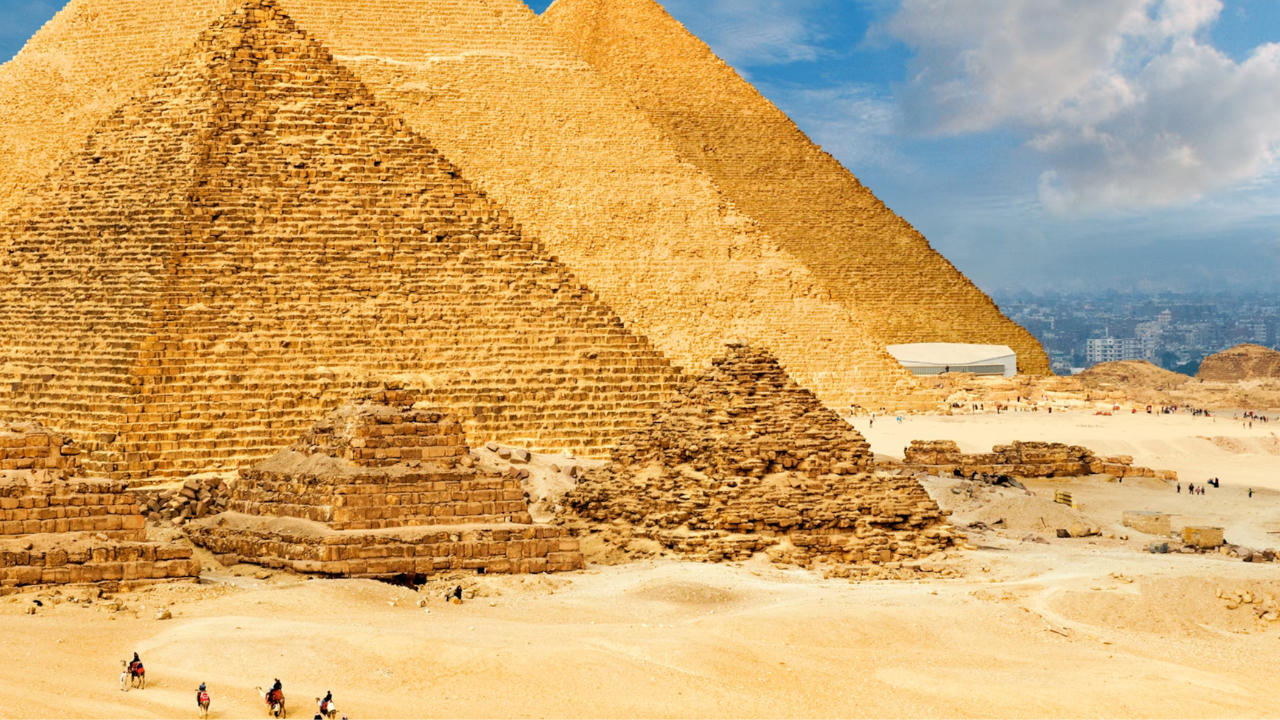

towering structures built as tombs for the pharaohs. The Great Pyramid of Giza, the largest pyramid ever built, is a testament to the Egyptians’ engineering prowess and their belief in the afterlife. The construction of these massive structures remains a source of wonder and speculation, with theories ranging from the use of ramps and levers to the involvement of extraterrestrial beings.
- The Great Pyramid of Giza: The largest pyramid ever built, a testament to Egyptian engineering.
- Construction techniques: The exact methods used to build the pyramids remain a subject of debate.
- Belief in the afterlife: The pyramids were built as tombs for the pharaohs, reflecting their belief in the afterlife.
The Gift of Hieroglyphics
Hieroglyphics, the ancient Egyptian writing system, is another fascinating aspect of Egyptian civilization.

This complex system of symbols was used to record everything from religious texts and historical events to personal accounts and business transactions. Deciphering hieroglyphics was a major breakthrough in Egyptology, allowing scholars to unlock the secrets of this ancient civilization.
- A complex system of writing: Hieroglyphics used thousands of symbols to represent different sounds and meanings.
- Record-keeping and communication: Hieroglyphics were used for a variety of purposes, including religious texts, historical records, and personal accounts.
- Deciphering hieroglyphics: The Rosetta Stone, a trilingual inscription, played a crucial role in deciphering hieroglyphics.
The Legacy of Ancient Egypt
The legacy of Ancient Egypt continues to captivate and inspire us today. The Egyptians’ achievements in art, architecture, science, and technology have had a profound impact on the world. Their enduring fascination with the afterlife, their belief in the power of the gods, and their ability to create stunning works of art and architecture have left an indelible mark on human history.
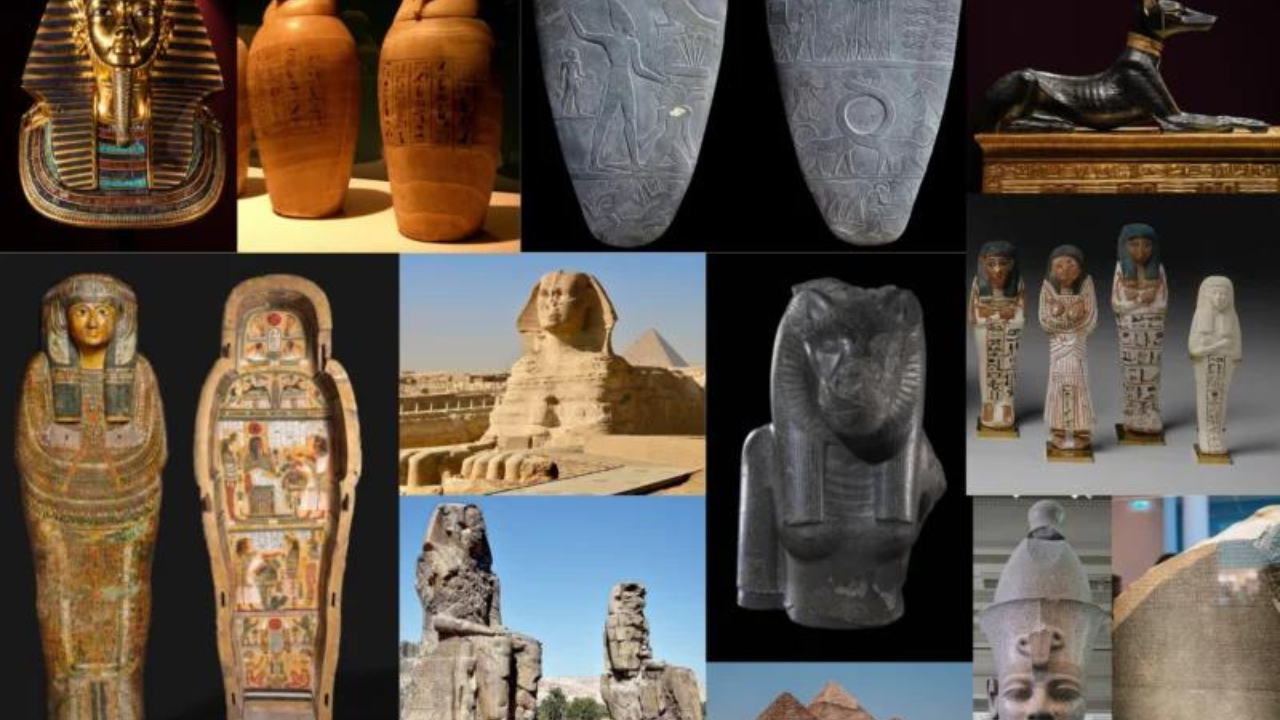

- Enduring fascination: The mysteries of Ancient Egypt continue to captivate people around the world.
- Contributions to art, architecture, science, and technology: The Egyptians made significant advancements in these fields.
- Legacy of belief in the afterlife: The Egyptians’ belief in the afterlife has influenced cultures throughout history.
The Art and Architecture of Ancient Egypt
Egyptian art and architecture are renowned for their beauty, complexity, and durability. The Egyptians were skilled sculptors, painters, and architects, and they created a wide range of works of art, including statues, reliefs, and paintings. Some of the most famous examples of Egyptian art include the bust of Nefertiti, the tomb paintings in the Valley of the Kings, and the temples of Karnak and Luxor.
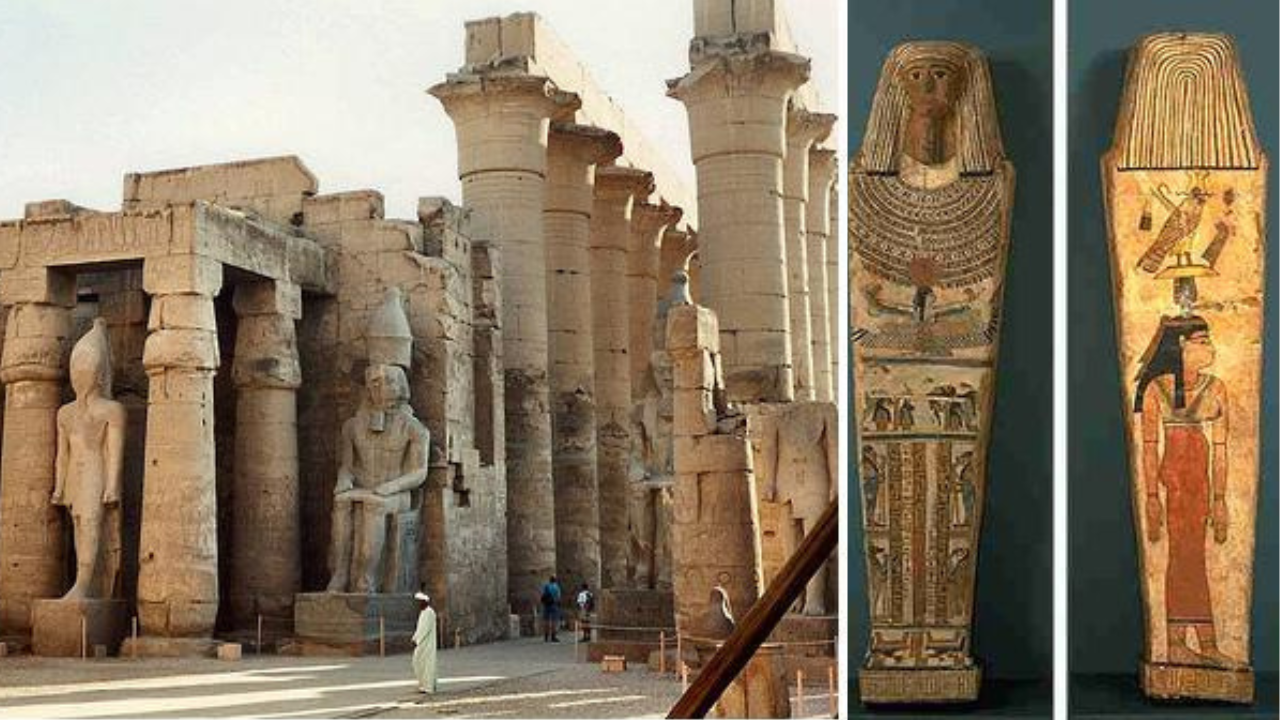

- Sculpture: The Egyptians were skilled sculptors who created realistic and detailed statues of pharaohs, gods, and other important figures.
- Painting: Egyptian painters used a variety of techniques to create vibrant and colorful murals and tomb paintings.
- Architecture: The Egyptians were master builders who constructed massive pyramids, temples, and palaces.
The Egyptian Economy and Society
The Egyptian economy was based on agriculture, trade, and manufacturing. The Nile River played a crucial role in Egyptian agriculture, providing fertile soil and water for irrigation. The Egyptians also engaged in trade with other civilizations, exporting goods such as papyrus, textiles, and precious metals. Egyptian society was hierarchical,
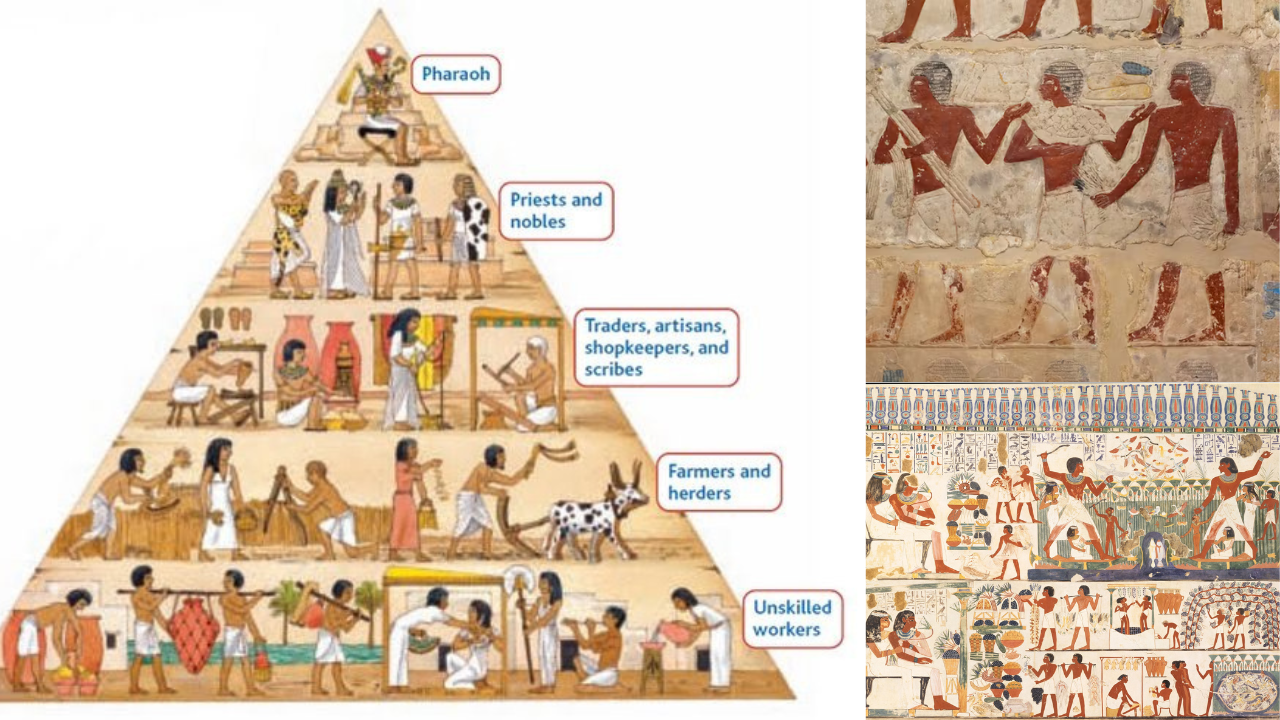
with the pharaoh at the top, followed by the nobility, priests, and commoners.
- Agriculture: The Egyptian economy was primarily based on agriculture, with the Nile River providing fertile soil and water.
- Trade: The Egyptians engaged in trade with other civilizations, exporting goods and importing raw materials.
- Social hierarchy: Egyptian society was divided into different social classes, with the pharaoh at the top.
The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Egypt
The legacy of Ancient Egypt continues to captivate and inspire us today. The Egyptians’ achievements in art, architecture, science, and technology have had a profound impact on the world. Their enduring fascination with the afterlife, their belief in the power of the gods, and their ability to create stunning works of art and architecture have left an indelible mark on human history.
By delving deeper into the mysteries of Ancient Egypt, we can gain a greater appreciation for this remarkable civilization and its contributions to the world. Whether you are a history buff, an art lover, or simply curious about the past, Ancient Egypt offers a fascinating journey of discovery.
Glossary
- Pharaoh: The ruler of Ancient Egypt, considered to be a divine king.
- Pyramid: A massive stone structure built as a tomb for a pharaoh.
- Hieroglyphics: The ancient Egyptian writing system.
- Rosetta Stone: A trilingual inscription that played a crucial role in deciphering hieroglyphics.
- Egyptology: The study of Ancient Egypt.
- Pantheon: A group of gods and goddesses.
- Mythology: A system of beliefs and stories about gods and heroes.
- Sculpture: The art of creating three-dimensional figures.
- Painting: The art of creating images on a surface.
- Architecture: The art and science of designing and constructing buildings.
- Agriculture: The cultivation of plants for food.
- Trade: The exchange of goods and services.
- Hierarchy: A system of ranking or classification.
FAQs
Q: When did Ancient Egypt exist?
A: Ancient Egypt existed for thousands of years, from approximately 3100 BCE to 30 BCE.
Q: Who were the most famous pharaohs of Ancient Egypt?
A: Some of the most famous pharaohs of Ancient Egypt include Khufu (Cheops), Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, Tutankhamun, and Ramses II.
Q: What is the significance of the pyramids?
A: The pyramids were built as tombs for the pharaohs and were a symbol of the Egyptians’ belief in the afterlife. They are also impressive feats of engineering.
Q: How were the pyramids built?
A: The exact methods used to build the pyramids remain a subject of debate, but it is believed that they were constructed using ramps and levers.
Q: What was the role of women in Ancient Egypt?
A: Women in Ancient Egypt enjoyed greater rights and opportunities than in many other ancient civilizations. They could own property, hold jobs, and even become pharaohs.
Q: What was the Egyptian religion?
A: The Egyptian religion was polytheistic, meaning they believed in many gods and goddesses. The most important gods included Ra (the sun god), Osiris (the god of the afterlife), and Isis (the goddess of motherhood).
Q: What was the Egyptian economy based on?
A: The Egyptian economy was based on agriculture, trade, and manufacturing. The Nile River played a crucial role in Egyptian agriculture, providing fertile soil and water for irrigation.
Q: What happened to Ancient Egypt?
A: The Egyptian Empire declined and fell due to a variety of factors, including internal strife, foreign invasions, and environmental challenges.
Q: What is the legacy of Ancient Egypt?
A: The legacy of Ancient Egypt continues to captivate and inspire us today. Their achievements in art, architecture, science, and technology have had a profound impact on the world.
